How do you use Pronouns in a Sentence?

Pronouns are special words we use instead of repeating other words, like names or objects. This helps to avoid saying the same things over and over again.
Pronouns can refer to people, animals, things, or ideas we’ve already talked about or know about.
Using pronouns makes our language clearer and shorter. They’re an essential part of English grammar. By using pronouns, we can make our sentences flow better and sound more natural.
It’s really important to understand how to use pronouns correctly so that we can communicate effectively. The following blog will explain to you a pronoun, their types, and their usage in a sentence
Let Us Know About The Types of Pronouns
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns refer to specific people or things. They change form based on number, person, and case subjective, objective, and possessive.
Subjective Case
Used as the subject of a sentence. I, you, he, she, it, we, and they.
For Example
She is going to the market.
Objective Case
Used as the object of a verb or preposition. Me, you, him, her, it, us, and them.
For Example
The teacher called him.
Possessive Case
Indicates ownership. My, your, his, her, its, our, and their.
For Example
That is her book.
Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns show ownership and do not require an apostrophe.
For Example
mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs
The book is mine.
Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and the object of a sentence are the same person or thing.
For Example
myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, and themselves.
She taught herself to play the piano.
Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns point to specific things and can be singular or plural.
For Example
this, that, these, those
These are my friends.
Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions.
For Example
who, whom, whose, which, what
Whose book is this?
Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns connect clauses or phrases to a noun or pronoun.
For Example
who, whom, whose, which, that
The man who called yesterday is my uncle.
Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns– refer to nonspecific people or things.
For Example
anyone, everyone, someone, no one, nobody, each, both, few, many, several
Everyone is welcome to the party.
Reciprocal Pronouns
Reciprocal pronouns are used when two or more people perform the same action.
For Example
each other, one another
They love each other.
Pronoun-Antecedent Agreement

The pronoun-antecedent agreement is a crucial rule in English grammar for maintaining coherence and clarity in sentences. This rule ensures that a pronoun matches its antecedent in number, gender, and person.
An antecedent is a noun to which a pronoun refers. Adhering to this rule prevents confusion in writing and helps to convey thoughts effectively.
It is important to recognize and apply the pronoun-antecedent agreement to avoid ambiguity and ensure a smooth flow of information in written communication.
Mastering this grammatical concept enhances the overall quality of one’s writing by fostering precision and accuracy.
For Example
Incorrect– Each student must bring their own book.
Correct– Each student must bring his or her own book.
Common Pronoun Mistakes

Pronouns are really important for making our language easier to use and less repetitive. But if you don’t use them correctly, they can also make things confusing. Using pronouns in the right way can make our sentences clearer and more comfortable.
Understanding the most common mistakes with pronouns and how to fix them can help you get better at writing and talking.
So let’s take a look at the most common mistakes and how to make them right.
- Misplaced Pronouns
Misplaced pronouns occur when it is not clear to which noun the pronoun is referring. This can lead to confusion and misunderstandings.
Ensure that pronouns clearly refer to the intended antecedent. If a sentence seems ambiguous, rephrase it to clarify the meaning. rewrite in easy language.
Misplaced pronouns happen when it’s not clear which noun the pronoun is supposed to refer to. This can confuse and lead to misunderstandings. Make sure that pronouns clearly point back to the right noun. If a sentence seems unclear, rephrase it to make the meaning clear.
For Example
Incorrect– When Jack gave his dog a bone, it wagged its tail.
‘It’ could refer to either Jack or the dog, which is confusing.
Correct– When Jack gave his dog a bone, the dog wagged its tail.
2. Ambiguous Pronouns
Ambiguous pronouns don’t tell us who they’re talking about, making it confusing for the reader.
When you use pronouns, make sure it’s clear which noun the pronoun is replacing. This helps the reader understand exactly what you’re talking about.
If there’s more than one possible thing the pronoun could be referring to, it’s best to repeat the noun to avoid confusion.
For Example
Incorrect– When Sam talked to Joe, he was upset.
It is unclear whether Sam or Joe was upset.
Correct– When Sam talked to Joe, Sam was upset.
Incorrect Pronoun Case
Pronouns come in different forms depending on their place in a sentence subject, object, or possessive. Using the right form is important for good grammar. Here’s how to remember.
Use words like I, you, he, she, it, we, and they when the pronoun is the subject.
Use words like me, you, him, her, it, us, and them when the pronoun is the object of a verb or a preposition.
For Example
Incorrect
Me and him went to the store.
‘Me’ and ‘him’ are objective cases, but they are used as subjects here.
Correct
He and I went to the store.
‘He’ and ‘I’ are subjective cases, appropriate for subjects.
Gender-Specific Pronouns

Gender-specific pronouns are words that show a specific gender, like ‘he’ for males and ‘she’ for females. They are used when we know the gender of the person. Sometimes using ‘he’ or ‘she’ when we don’t know the gender can be wrong or hurtful.
In some situations, using gender-specific pronouns can leave out people who don’t identify as strictly male or female.
Incorrect
If someone loses his ticket, he cannot enter.
Correct
If someone loses their ticket, they cannot enter.
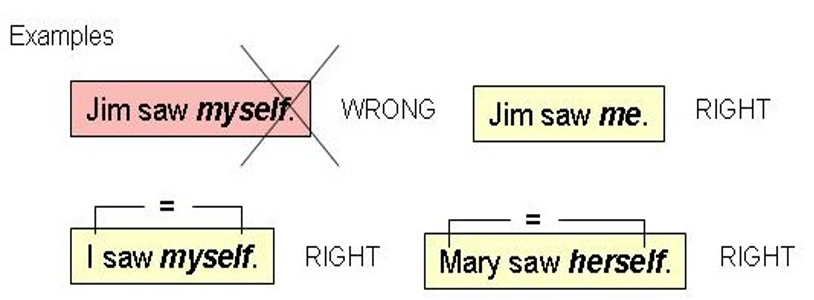
Reflexive Pronoun Errors
Reflexive pronouns are words like myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, and themselves. They are used when the subject of the sentence is also the receiver of the action.
For example, I hurt myself. It’s important not to use reflexive pronouns when they are not needed, such as saying ‘Myself and John went to the store’ instead of ‘John and I went to the store.’
It’s also incorrect to replace personal pronouns with reflexive pronouns, like saying ‘Myself did it’ instead of ‘I did it.’
For Example
Incorrect
Sarah and myself went to the meeting.
Correct
Sarah and I went to the meeting.
Incorrect
He made dinner for myself and my friends.
Correct
He made dinner for me and my friends.
Inconsistent Pronoun Use
Sometimes, we can confuse the reader by using different words to talk about the same thing. Let us consider if we start talking about something, and then suddenly switch to using a different word for it, it can make it hard for the reader to understand.
It’s like if I start talking about a cat and then call it ‘it’ and then ‘she’ in the same sentence. That can be confusing. It’s important to stick to using the same word to talk about the same thing to avoid confusion.
For Example
Incorrect
When a student submits their essay, he or she should ensure it is proofread.
Correct
When a student submits his or her essay, he or she should ensure it is proofread.
Overuse of Pronouns

Using pronouns too often can make sentences confusing and hard to follow. When there are too many pronouns in a sentence, and it’s not clear what they are referring to, the reader can get confused.
It’s important to make sure that pronouns have clear antecedents, which means they should clearly refer back to a specific noun. When pronouns are used without a clear antecedent, it can be difficult to understand who or what is being talked about in a sentence.
For Example
Incorrect
She went to the store because she needed it for her project, but she forgot it.
Correct
Jane went to the store because she needed materials for her project, but she forgot the list.
CONCLUSION
Using pronouns correctly in sentences is essential for clear and effective communication. Pronouns must agree with their antecedents in number, gender, and person to avoid confusion and ensure coherence.
By identifying and correctly matching antecedents, avoiding ambiguous or misplaced pronouns, and maintaining consistency, writers can enhance the readability of their text. Gender-neutral pronouns help promote inclusivity, while proper use of reflexive pronouns and personal pronouns ensures grammatical accuracy.
Regular practice and attention to these details will make pronoun usage second nature, allowing for more fluid and understandable writing. By mastering pronoun use, you contribute to clearer, more concise, and engaging communication, making your writing more accessible and enjoyable for readers.






